Introduce the topic of mimicry plants, what they are, and why they are important.
Mimicry plants are important because they help camouflage animals and protect them from predators. They also play an important role in the food chain. Many animals depend on mimicry plants for their survival.
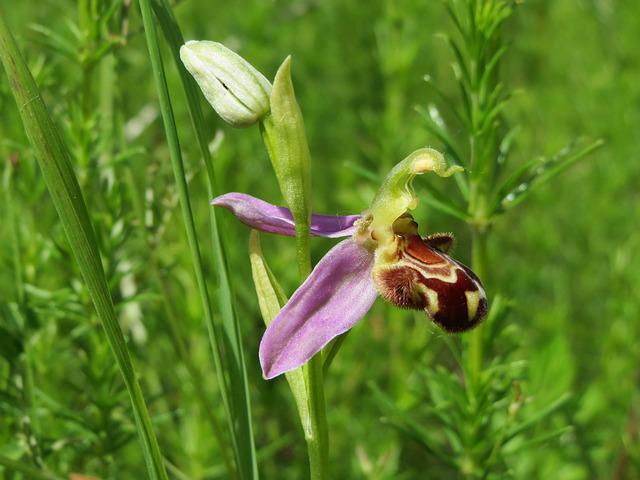

Groups of plants are mimicry plants. Mimicry plants are so named because they look like something else. There are many different types of mimicry, but all involve some aspect of disguise. For example, some mimicry plant look like animals, while others look like other plant. However, all these plants have in common because they use their appearance to avoid being eaten or attacked.
Mimicry plants have evolved in response to the threats posed by herbivores and predators. These plants can avoid being eaten or attacked by looking like something else. This is an important survival strategy, as it allows these plants to escape the attention of predators and herbivores. Mimicry also allows these plants to take advantage of resources otherwise unavailable to them.
An Overview of mimicry plants
Mimicry plants, also known as mimics, are a type of plant that has evolved to look like other plants. There are two types of mimicry plants: Batesian and Müllerian. Batesian mimicry plants imitate harmless species to avoid being eaten by predators, while Müllerian mimicry plants imitate unpalatable or dangerous species to reduce the chance of being eaten. plants can be found worldwide, and some are very well-known for their unusual appearance.
Description of mimicry plants
Mimicry plants are a fascinating group that has evolved to look like other plants. Mimicry plants can be found worldwide and come in many different shapes and sizes.
One of the most well-known types of mimicry plants is the Venus flytrap. This plant has evolved to look like a small, green leaf. The Venus flytrap can catch its prey by closing its trap-like leaves around the unsuspecting insect.
Another common type of mimicry plant is the pitcher plant. This plant has pitcher-shaped leaves that collect rainwater and insects. The pitcher plant uses these insects as a source of food.
Lithops as mimicry plant succulent
Lithops, commonly called Living Stones, are a genus of succulent plants in the Aizoaceae family. There are about 125 species of Lithops. These plants are native to southern Africa. Lithops are popular as houseplants and can be found in many nurseries.
One of the reasons Lithops are so popular is because they mimic other rocks and stones. This allows them to blend into their environment and avoid being eaten by animals. In addition, some believe that the markings on different Lithops species resemble eyes, which helps to camouflage the plant further.
14 types of mimicry plants
Mimicry plants are a fascinating group of plants that have evolved to look like other objects in their environment. There are 14 different types of mimicry plants, each with a unique way of fooling predators.
One type of mimicry plant is the stick mimetic plant. These plants look like sticks, and they often grow in areas that are covered in dried leaves. When a predator comes near, the plant will wiggle its “stick” to make it look like an animal moving.
Another type of mimicry plant is the flower mimetic plant. These plants often look like flowers but have a different smell than actual flowers. This can confuse predators, who may be unable to tell the difference between a real and fake flower.
Mimicry plants 1 Lithops spp. (living rocks)
Lithops spp. (living rocks) are a fascinating and unique plant genus that is endemic to Southern Africa. The plants in this genus have evolved to mimic the surrounding rocks and soil, with their green or brownish leaves resembling small pebbles. Lithops spp. are succulents, meaning they store water in their leaves and can survive long periods of drought.
The flowers of Lithops spp. are also very unusual, with the petals appearing as small black dots on the leaf’s surface. The flowers usually only open for a short period, releasing pollen onto the stigma of another flower—Lithops spp. Reproduce through seed, and new plants can take up to five years to reach maturity.
Despite their unusual appearance, Lithops spp.
Mimicry plants 2 Fenestraria aurantiaca
Mimicry plants are a unique group of plants that have evolved to look like other objects in their environment. For example, the mimicry plant is the Fenestraria aurantiaca, which mimics the color and texture of an orange. This plant has evolved to look like this fruit to avoid being eaten by animals. Other examples of mimicry plants include the pitcher plant, which mimics the color and shape of a pitcher, and the Venus flytrap, which mimics the color and shape of a Venus flytrap.
Mimicry plants 3 Pleiospilos nelii ‘Royal Flush.
One of the more interesting and exotic plants in the succulent hobby is the mimicry plant. Several genera of plants belong to this group, but the most popular is Pleiospilos Alii, also known as the “Royal Flush” plant. This succulent grows in a rosette formation and has green leaves on top and purplish-gray on the bottom. The flowers are yellow with brown spots and grow in clusters on tall stalks.
What makes Pleiospilos nelii so unique is its ability to mimic other plants. It can often be found growing next to rocks or different succulents, where it will take on the coloration of its surroundings. This helps to protect it from being eaten by predators or getting too much sun exposure.
Mimicry plants 4 Titanopsis calcareum
One of the most interesting plants to observe is the mimicry plant. Titanopsis calcareum is a prime example of this type of plant. This succulent has a smooth, grayish-green surface that helps it blend in with the surrounding rocks. This plant is special, though, because it can change color in response to its environment. If it’s in a sunny spot, the Titanopsis will turn deep green, but if it’s moved to a shady area, it will become pale green or white. This ability to adapt makes it very difficult for predators to find them.
Mimicry plants 5 Lapidaria margaretae (the Karoo rose)
Mimicry plant are fascinating organisms that have evolved to look like other plants or animals. One such example is the Karoo rose, Lapidaria margaretae. This plant has grown to look like a rock, which helps it blend in with its surroundings and avoid being eaten by herbivores. The leaves of the Karoo rose are covered in small bumps and ridges, which help break up the plant’s outline and make it look more like a rock. The flowers of the Karoo rose are also very striking, with their bright pink petals and contrasting yellow centers.
Mimicry plants 6 Flypaper plant (Mirabilis jalapa)
The flypaper plant is a unique-looking plant that can be found in many gardens. This plant got its name from the sticky sap that covers its leaves. If you touch the leaves, your fingers will be covered in liquid. The juice is used to trap insects, which the plant then eats. The flypaper plant is a type of mimicry plant. Mimicry plants are plants that copy the appearance of other plants to fool predators into thinking they are something else.
Mimicry plants 7 Deceptive unguent plant (Liatris spicata)
Liatris spectra, commonly known as the gayfeather, is a North American herbaceous plant in the sunflower family. It is a perennial that grows from 0.5-2 m (1.6-6.6 ft) tall, with a branching stem and a few leaves near the base. The leaves are lanceolate to linear, up to 40 cm (16 in) long and 2 cm (0.8 in) wide, and have smooth margins. The plant produces several flower heads, each about 3 cm (1.2 in) in diameter, containing many small disc flowers. The fruit has an achene about 1 mm (0.
Mimicry plants 8 Rafflesia arnoldii
Mimicry plants are a fascinating and little-known group of plants that have evolved to look like other objects in their environment. There are many different types of mimicry plants, but the most common is probably the leaf mimicry plant. These plants have leaves that look like the leaves of other plants in their environment, allowing them to blend in and avoid being eaten.
One of the best-known examples of a mimicry plant is Rafflesia arnoldii, the corpse flower. This plant is found in Southeast Asia and has a large, fleshy flower that looks like a rotting corpse. The smell of this flower is so bad that it can be used to repel animals from entering an area.
Mimicry plants 9 Purple false indigo.
Mimicry plants are an interesting group of that have evolved to look like other objects in their environment. One example of a mimicry plant is the purple false indigo. This plant has grown to look like a dead leaf, which helps it avoid being eaten by animals. Another example of a mimicry plant is the Venus flytrap. This plant has evolved to look like a dead animal, which helps it catch prey. Mimicry plants are a fascinating group of plants and are important for understanding how evolution works.
Mimicry plants 10 White spotted deerberry (Elaeagnus umbellata)
Mimicry plants are a fascinating group of plants that have evolved to look like other objects in their environment. One of the most common mimicry plants is those resembling animals. White-spotted deerberry is a good example of this type of plant. It has small, white berries that look like the spots on a deer’s back. This plant is found throughout North America and can be easily identified by its distinctive berries.
Mimicry plants 11 Bleeding heart vine (Clerodendrum speciosissimum)
The bleeding heart vine is a tropical found in the rainforest and other humid environments. It is known for its beautiful flowers, which resemble the bleeding heart flower. The leaves of the vine also resemble those of the bleeding heart flower.
The bleeding heart vine is a mimicry plant. This means that it mimics other plants to avoid being eaten by predators. The leaves of the vine look like the leaves of the bleeding heart flower, which may confuse predators into thinking that they are eating a flower, not a leaf. The vine’s buds also look like the flowers of the bleeding heart, which may confuse predators into thinking that they are eating a flower, not a fruit.
Mimicry plants 12 False sensitive plants (Mimosa diplotricha)
False sensitive plants are so named because they fold their leaves when touched, but this reaction is not caused by sensitivity to connect but is a defense mechanism to avoid being eaten. The leaves fold up to form a little ball, making it more difficult for animals to eat them. False sensitive plants are found in Africa, Asia, and Australia.
Mimicry plants 13 Venus flytraps.
The Venus flytrap is a well known example of a mimicry plant. This carnivorous has leaves that look like the heads of insects, which lures in prey. Once an insect touches the leaves, the Venus flytrap snaps shut, trapping the insect inside. The plant then dissolves the insect in digestive juices to extract its nutrients.
What Are Mimicry Succulents?
These succulents have leaves that look like those of different plants and may even smell like them. This defense mechanism helps the plant avoid being eaten by animals. Mimicry succulents can be found in many parts of the world, and they come in various shapes and colors.
How to care for your new mimicry succulent
The mimicry succulent is a beautiful new addition to any garden, but it requires some special care to stay healthy and look its best. Here are a few tips to get you started:
- Mimicry Succulents need plenty of sunlight. Therefore, please place them where they will receive at least six hours of direct sunlight each day.
- They also need regular watering. Do not let the plant sit in waterlogged soil for extended periods.
- Fertilize your plant once a month with a balanced fertilizer diluted to half strength
- In the winter, mimicry succulents can be kept indoors near a sunny window; in the summer, they should be moved back outdoors.
An Exception Faucaria
The Faucaria is a succulent that is native to South Africa. One of the most interesting things about this plant is its ability to mimic other plants in its environment. For example, the Faucaria plant has leaves shaped like tiger claws, which gives it its common name, “tiger’s claw.” This plant can also change the color of its leaves depending on its environment. If it is in a sunny location, the leaves will be green. If it is in a shady spot, the leaves will be brown.
Types of Mimicry Plants: Discuss the different kinds of mimicry plant and give a few examples.
Mimicry plant are a type of plant that has evolved to look like other objects in their environment. This can serve as a protection, as the plant can blend in and avoid being eaten. There are several different types of mimicry plants, including camouflage, resemblance, and mimesis.
Camouflage is the most common type of mimicry. Plants that use this strategy typically have leaves or flowers that match the color of their surroundings. For example, the Virginia Creeper vine has green leaves that blend in with the trees it grows on, and the Evening Primrose flower is pale yellow and blends in with the background of soil and grasses.
The resemblance is another type of mimicry employed by plants. These plants look like something else but don’t necessarily match the color of their surroundings.
How to Care for Mimicry Plant: Offer tips on caring for mimicry plant, including watering, light, and soil requirements.
Mimicry plants may be a perfect choice if you’re looking for an interesting and exotic houseplant. These plants are characterized by their ability to mimic other plant species, often with startling accuracy. While care for mimicry plant may vary depending on the species, some general tips can help you keep your plant healthy and looking its best.
One of the most important things to remember when caring for mimicry plants is to water them regularly. They typically need more water than other houseplants, so check the soil regularly and water as needed. Another key factor in keeping your mimicry plant healthy is providing the right amount of sunlight. They need at least six hours of direct sunlight per day, so place them in a spot where they will get plenty of natural light.
Using Mimicry Plant in Your Garden: Share ideas on using mimicry plants in your garden, including planting them in containers or incorporating them into flower beds.
Mimicry plants can add a touch of interest to any garden. By planting them in containers or incorporating them into your garden design, you can enjoy their beauty and also benefit from their ability to confuse pests.
One way to use mimicry plant is to grow them in containers on your porch or patio. This way, you can enjoy their color and shape up close, and the plants will also help keep pests away from your other plants.
Another option is to use mimicry plants as part of your garden design. For example, you could plant a group of tall plants in the back of your garden and then use smaller plants in front that resemble insects or other animals. This will add interest and confusion to your garden while also helping deter pests.
How to care for mimicry plants: Tips to keep them thriving
Mimicry plants, also known as Venus flytrap plants, are a type of carnivorous plant that trap and digest insects to extract their nutrients. They are easy to care for and can thrive in various conditions, but there are some tips you can follow to keep them healthy and thriving.
The first thing you’ll need to do is make sure your mimicry plant gets enough light. You can supplement with grow lights if you can’t provide that light.
You’ll also need to water your plant regularly. Mimicry plants like wet soil but don’t like to sit in waterlogged soil. Please ensure the ground is moist but not wet and don’t overwater them.
Types of mimicry plants: Why are they so effective?
Mimicry plants have developed effective methods of survival. One way they protect themselves is by resembling other, more harmful plants. This is known as mimicry. There are several different types of mimicry plants, and each has a unique way of protecting itself from predators.
Some mimicry plants resemble poisonous species. These plants have evolved to produce toxins that make them unpalatable or even deadly to animals. By looking like a toxic plant, the mimicry plant reduces the chances that a predator will eat it.
Other mimicry plants look like unappetizing or inedible plants. These species may not produce toxins, but they still benefit from their resemblance to less desirable plants. Predators that avoid eating all plants may leave these mimics alone, allowing them to grow and reproduce successfully.
Conclusion: Summarize what has been discussed and offer final thoughts on mimicry plants.
Mimicry plants are fascinating creatures that have evolved to look like other plants to avoid being eaten. They can be found worldwide, and while they may not be as flashy as some of their more colorful counterparts, they are nonetheless intriguing. Mimicry plants have several strategies to avoid being eaten, and while many of them are still being studied, scientists have learned a great deal about these unique plants. In addition to their ability to avoid being eaten, mimicry plants also play an important role in the ecology of their respective ecosystems. They provide food for animals, help with pollination, and contribute to the overall health of their habitats. While scientists continue to study mimicry plants, they are undoubtedly one of the most interesting and underappreciated groups of organisms on Earth.










Commented Posts